Traffic flow within NSX
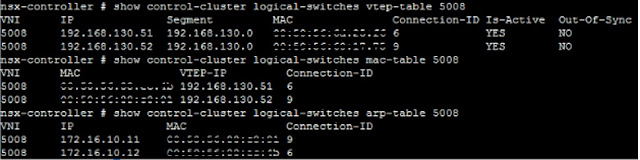
Below article details the traffic flow that happens within NSX Host preparation process during NSX installation creates the VXLAN (netcpa) and firewall (vsfwd) capabilities within every host or cluster. Thus every host gets ready to operate NSX attributes. Transport Zone are considered as the boundary of the VXLANs or the logical switches. Whenever a logical switch is created it is attached to a Transport Zone (Global or Universal). Since the hosts or the clusters are VXLAN ready thus they communicate with NSX Controllers through User World Agent (UWA) process that operates via netcpa services. NSX Controllers are privotal in NSX architecture and are part of control plane of NSX architecture as they build and retain VTEP table, MAC table and ARP table for every VNI or VXLAN. In case any host that is not having any of these information first contacts NSX Controllers to gain respective destination MAC/IP details. NSX Controllers on the other hand build these tables (VTEP tabl...